
MySQL DBaaS vs MySQL in Azure VM
MySQL DBaaS vs MySQL in Azure VM
With Azure, your MySQL server workloads can run in a hosted virtual machine infrastructure as a service (IaaS) or as a hosted platform as a service (PaaS). PaaS has multiple deployment options, and there are service tiers within each deployment option. When you choose between IaaS and PaaS, you must decide if you want to manage your database, apply patches, and make backups, or if you want to delegate these operations to Azure.
When making your decision, consider the following two options:
- Azure Database for MySQL. This option is a fully managed MySQL database engine based on the stable version of MySQL community edition. This relational database as a service (DBaaS), hosted on the Azure cloud platform, falls into the industry category of PaaS.
With a managed instance of MySQL on Azure, you can use built-in features that otherwise require extensive configuration when MySQL Server is either on-premises or in an Azure VM.
When using MySQL as a service, you pay as you go with options to scale up or scale out for greater control with no interruption. And unlike standalone MySQL Server, Azure Database for MySQL has additional features like built-in high availability, intelligence, and management.
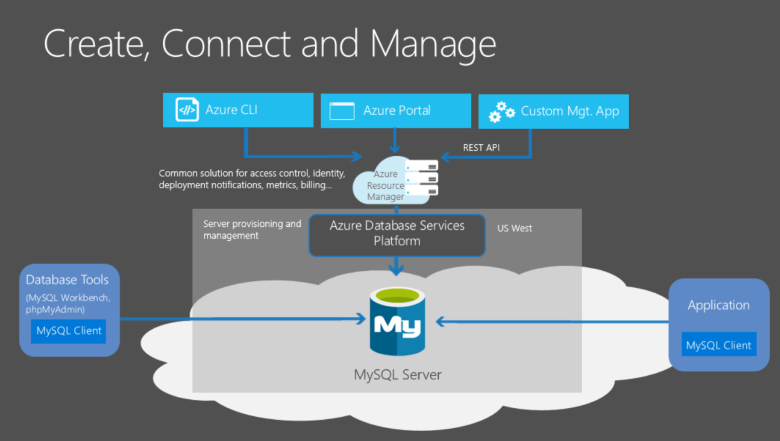
- MySQL on Azure VMs. This option falls into the industry category of IaaS. With this service, you can run MySQL Server inside a fully managed virtual machine on the Azure cloud platform. All recent versions and editions of MySQL can be installed on an IaaS virtual machine.
In the most significant difference from Azure Database for MySQL, MySQL on Azure VMs offers control over the database engine. However, this control comes at the cost of responsibility to manage the VMs and many database administration (DBA) tasks. These tasks include maintaining and patching database servers, database recovery, and high-availability design.
The main differences between these options are listed in the following table:
| TABLE 1 | ||
| Azure Database for MySQL | MySQL on Azure VMs | |
| Service-level agreement (SLA) | Offers SLA of 99.99% availability |
Up to 99.95% availability with two or more instances in the same availability set. 99.9% availability with a single instance VM using premium storage. 99.99% using Availability Zones with multiple instances in multiple availability sets. See the Virtual Machines SLA. |
| Operating system patching | Automatic | Managed by customers |
| MySQL patching | Automatic | Managed by customers |
| High availability | The high availability (HA) model is based on built-in failover mechanisms for when a node-level interruption occurs. In such cases, the service automatically creates a new instance and attaches storage to this instance. | Customers architect, implement, test, and maintain high availability. Capabilities might include clustering,replication etc. |
| Zone redundancy | Currently not supported | Azure VMs can be set up to run in different availability zones. For an on-premises solution, customers must create, manage, and maintain their own secondary data center. |
| Hybrid scenarios |
With Data-in Replication, you can synchronize data from an external MySQL server into the Azure Database for MySQL service. The external server can be on-premises, in virtual machines, or a database service hosted by other cloud providers. With the read replica feature, you can replicate data from an Azure Database for MySQL master server to up to five read-only replica servers. The replicas are either within the same Azure region or across regions. Read-only replicas are asynchronously updated using binlog replication technology. |
Managed by customers |
| Backup and restoration | Automatically creates server backups and stores them in user-configured storage that is either locally redundant or geo-redundant. The service takes full, differential, and transaction log backups | Managed by customers |
| Monitoring database operations | Offers customers the ability to set alerts on the database operation and act upon reaching thresholds. | Managed by customers |
| Advanced Threat Protection | Provides Advanced Threat Protection. This protection detects anomalous activities that indicate unusual and potentially harmful attempts to access or exploit databases. | Customers must build this protection for themselves. |
| Disaster recovery | Stores automated backups in user-configured locally redundant or geo-redundant storage. Backups can also restore a server to a point in time. The retention period is anywhere from 7 to 35 days. Restoration is accomplished by using the Azure portal. | Fully managed by customers. Responsibilities include but aren’t limited to scheduling, testing, archiving, storage, and retention. An additional option is to use an Azure Recovery Services vault to back up Azure VMs and databases on VMs. This option is in preview. |
| Performance recommendations | Provides customers with performance recommendations based on system-generated usage log files. The recommendations help to optimize workloads. | Managed by customers |
Business motivations for choosing PaaS or IaaS
There are several factors that can influence your decision to choose PaaS or IaaS to host your MySQL databases.
Cost
Limited funding is often the primary consideration that determines the best solution for hosting your databases. This is true whether you’re a startup with little cash or a team in an established company that operates under tight budget constraints. This section describes billing and licensing basics in Azure as they apply to Azure Database for MySQL and MySQL on Azure VMs.
Billing
Azure Database for MySQL is currently available as a service in several tiers with different prices for resources. All resources are billed hourly at a fixed rate. For the latest information on the currently supported service tiers, compute sizes, and storage amounts, see vCore-based purchasing model. You can dynamically adjust service tiers and compute sizes to match your application’s varied throughput needs. You’re billed for outgoing Internet traffic at regular data transfer rates.
With Azure Database for MySQL, Microsoft automatically configures, patches, and upgrades the database software. These automated actions reduce your administration costs. Also, Azure Database for MySQL has built-in backup capabilities. These capabilities help you achieve significant cost savings, especially when you have a large number of databases. In contrast, with MySQL on Azure VMs you can choose and run any MySQL version. No matter what MySQL version you use, you pay for the provisioned VM and the costs for the specific MySQL license type used.
Azure Database for MySQL provides built-in high availability for any kind of node-level interruption while still maintaining the 99.99% SLA guarantee for the service. However, for database high availability within VMs, customers should use the high availability options like MySQL replication that are available on a MySQL database. Using a supported high availability option doesn’t provide an additional SLA. But it does let you achieve greater than 99.99% database availability at additional cost and administrative overhead.
Administration
For many businesses, the decision to transition to a cloud service is as much about offloading complexity of administration as it is about cost. With IaaS and PaaS, Microsoft:
- Administers the underlying infrastructure.
- Automatically replicates all data to provide disaster recovery.
- Configures and upgrades the database software.
- Manages load balancing.
- Does transparent fail-over if there’s a server failure.
The following list describes administrative considerations for each option:
- With Azure Database for MySQL, you can continue to administer your database. But you no longer need to manage the database engine, the operating system, or the hardware. Examples of items you can continue to administer include:
- Databases
- Sign-in
- Index tuning
- Query tuning
- Auditing
- Security
Additionally, configuring high availability to another data center requires minimal to no configuration or administration.
- With MySQL on Azure VMs, you have full control over the operating system and the MySQL server instance configuration. With a VM, you decide when to update or upgrade the operating system and database software. You also decide when to install any additional software such as an antivirus application. Some automated features are provided to greatly simplify patching, backup, and high availability. You can control the size of the VM, the number of disks, and their storage configurations. For more information, see Virtual machine and cloud service sizes for Azure.
Time to move to Azure
- Azure Database for MySQL is the right solution for cloud-designed applications when developer productivity and fast time to market for new solutions are critical. With programmatic functionality that is like DBA, the service is suitable for cloud architects and developers because it lowers the need for managing the underlying operating system and database.
- When you want to avoid the time and expense of acquiring new on-premises hardware, MySQL on Azure VMs is the right solution for applications that require a MySQL database or access to MySQL features on Windows or Linux. This solution is also suitable for migrating existing on-premises applications and databases to Azure intact, for cases where Azure Database for MySQL is a poor fit.
Because there’s no need to change the presentation, application, and data layers, you save time and budget on re-architecting your existing solution. Instead, you can focus on migrating all your solutions to Azure and addressing some performance optimizations that the Azure platform might require.
For any consulting requirements, please email us on cloud@proarch.com